 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this section, we’ll review measures of two- and three-dimensional figures by determining how changes in one or more of a figure’s dimensions will influence those measures.
We need to find a way to represent the doubled length and width. (Now’s a good time to note that length and width and base and height may be used interchangeably. So the area of a parallelogram is also given by the formula A = lw.)
If l is the length, then 2l is the doubled length. Similarly, if w is the width, then 2w is the doubled width. Now just substitute the new length and new width into the formula where the old length and old width were.
The new area is:
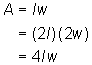
One more? How is the volume of a cone affected if the radius is doubled and the height is divided by two? What are your initial thoughts? Do you think the volume will be affected?
The volume of a cone is given by the formula 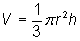 , where r is the radius of the base and h is the height. The doubled radius can be represented by 2r and the halved height can be represented by
, where r is the radius of the base and h is the height. The doubled radius can be represented by 2r and the halved height can be represented by 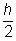 . The new volume is:
. The new volume is:
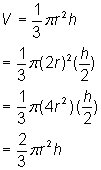
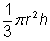 , and the new volume is
, and the new volume is 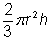 . The new volume is twice the old volume.
. The new volume is twice the old volume.
How is the area of an isosceles right triangle affected if the length of each leg is doubled?
Choice C is the correct answer. The area of a triangle is given by the formula 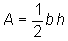 , where b is the base and h is the height. The base and height of an isosceles right triangle are its legs, so the area of the triangle for which the lengths of the legs are doubled is:
, where b is the base and h is the height. The base and height of an isosceles right triangle are its legs, so the area of the triangle for which the lengths of the legs are doubled is:
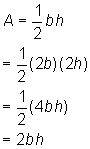
The area of the old triangle was 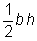 and the area of the new triangle is 2bh. That means if the lengths of the legs of an isosceles right triangle are doubled, the area of the new triangle will be four times the area of the old triangle.
and the area of the new triangle is 2bh. That means if the lengths of the legs of an isosceles right triangle are doubled, the area of the new triangle will be four times the area of the old triangle.
The metric system is a decimal system of measurement, which means that all metric units are based on multiples of ten. For example, a kilometer is 1,000 meters and 10 millimeters equal one centimeter.
The metric system is also called the International System of Units (abbreviated SI, for its name in French). So, metric and SI are used interchangeably.
This table gives the most common metric prefixes and their meanings:
| Prefix | Symbol | Meaning (multiply by) |
|---|---|---|
| kilo- | k | 1000 |
| centi- | c | 0.01 = 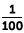 |
| milli- | m | 0.001 = 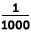 |
The metric unit of length is the meter (m); the metric unit of mass is the kilogram (kg); and the metric unit of volume is the liter (l).
For example, 1 m = 100 cm, 1 mg = 0.001 g, and 1000 l = 1 kl.
Although the SI unit of temperature is the Kelvin, most often, the Celsius scale is used to measure temperatures where this system is used. These are common temperatures:
The customary system is the system we’re accustomed to in the United States. It’s also called the English system or the standard system. Customary units of length include the inch (in.), foot (ft), and mile (mi); customary units of weight include the ton (t), the pound (lb), the ounce (oz); and customary units of capacity include fluid ounces (fl. oz), pints (pt), cups (c), and quarts (qt).
You’re likely familiar with these relationships among customary units:
Most often, the Fahrenheit scale is used to measure temperatures where this system is used. These are common temperatures:
These facts may give you a better sense of the relationships between these systems:
And here’s how we convert between the Fahrenheit and Celsius temperature scales:
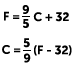
Which of the following lengths is greatest?
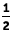 ft
ftChoice A is the correct answer. Fifteen cm is about six in.; 125 mm equals 12.5 cm, which is about 5 inches; and 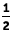 ft equals 6 in. Of the measures given, seven in. is the greatest.
ft equals 6 in. Of the measures given, seven in. is the greatest.
The basic units given in each of the systems above are called simple units. Simple units can be put together to derive units of measurement for other quantities. Naturally, these put-together units are called derived units.
This may sound more complicated than it is. Miles per hour is a derived unit. So are square meters, hours per week, people-hours, and kilogram-meters per second squared. (See, some are more derived than others.) In fact, a kilogram-meter per second squared is called a Newton, so a Newton is also a derived unit, even though it looks simple.
Rate is equal to the quotient of distance and time, or 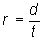 . Which of the following is a unit of rate?
. Which of the following is a unit of rate?
Choice D is the correct answer. A unit of rate is equal to a unit of distance divided by a unit of time. A meter is a unit of distance and a second is a unit of time, so 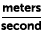 , or meters per second, is a unit of rate.
, or meters per second, is a unit of rate.