 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson, you will learn about asexual and sexual reproduction. Scientists, regardless of their specialization, need to possess a basic level of science literacy across all disciplines. This lesson provides an overview of the major concepts pertaining to reproduction that all students of the sciences should know. The chapters that follow will focus in greater detail on these ideas.
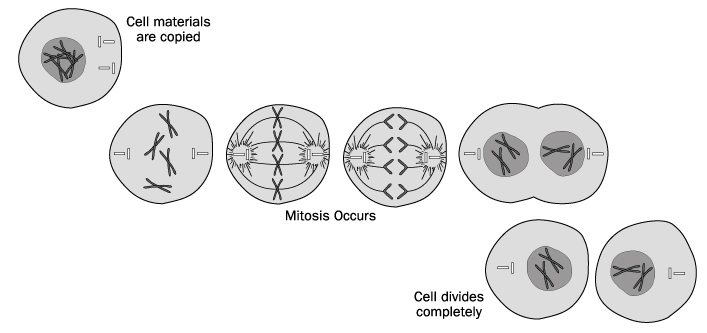
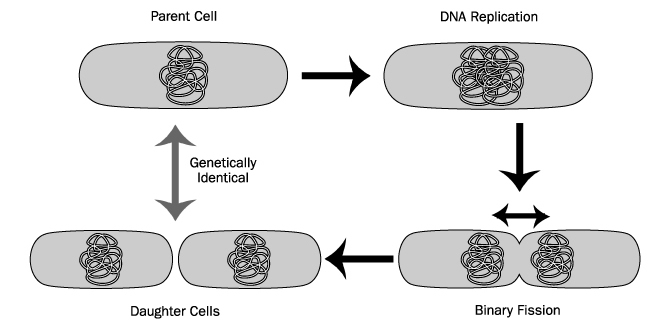
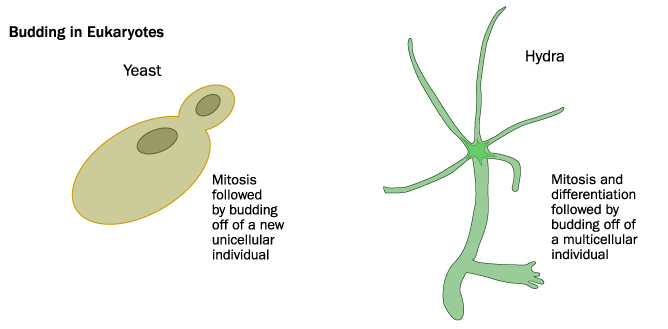

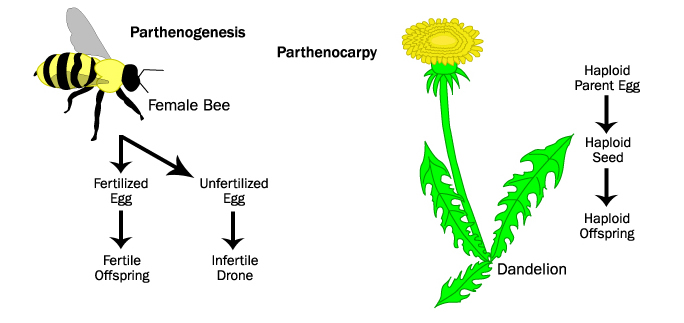
Simple prokaryotic organisms reproduce asexually, usually via which mode?
Hope you chose D. While choices A, B, and C are asexual modes of reproduction, binary fission is the most common.
Sexual reproduction is characterized by meiosis and fusion of two genetically unique gametes to form a unique offspring. Self pollination of a flower is a form of sexual reproduction, because the flower has both male and female reproductive structures that produce unique gametes.
Organisms that reproduce sexually must reduce their number of chromosomes by half via meiosis at some point during their life cycle. Sexual reproducers have one of three distinct life cycles:
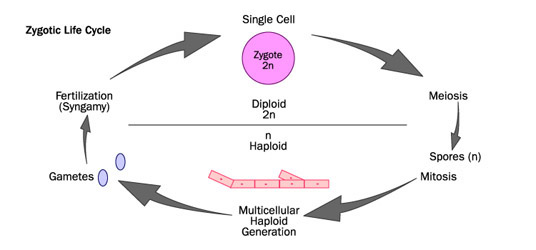
The zygote is the only diploid form of the organism. It quickly undergoes meiosis to produce the dominant haploid form. All sexually reproducing fungi and some algae have zygotic life cycles.
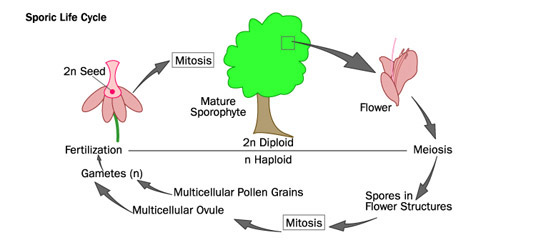
There is a true alternation of generations, such that both the diploid and haploid forms undergo mitosis to produce multicellular forms. Some algae and all plants have sporic life cycles. In primitive nonvascular plants, such as mosses, the haploid form is dominant. In seed plants, the diploid form is dominant.
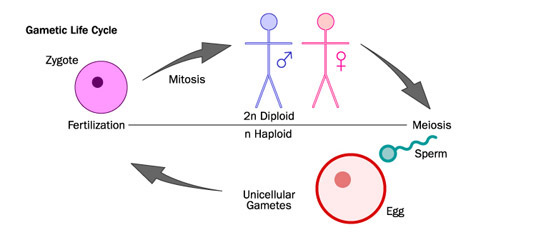
The gamete is the only haploid form of the organism, and it is always unicellular. Most animals, including humans, have gametic life cycles.
What is transduction?
The correct answer is C. Choice A defines mutation, choice B defines conjugation, and choice D defines transformation.
When gametes are produced via meiosis in sexually reproducing organisms, genetic variation is introduced in several ways.
Syngamy produces a unique diploid zygote.
Crossing-over of homologous chromosomes during prophase 1 leads to genetic recombination and formation of unique chromosomes.
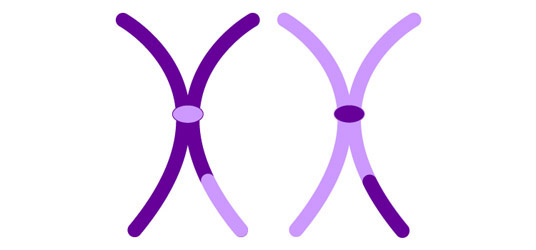
Which is the source of genetic variation in organisms that reproduce asexually?
The correct answer is D. Choices A-C all reflect processes that occur only in sexually reproducing organisms. Mutation is the ultimate source of all genetic variation of all living things.
Asexual reproduction is advantageous in several ways. It allows very fast, energetically inexpensive production of many genetically identical offspring in organisms, such as bacteria and simple eukaryotes. If the organisms in question are well-adapted to a relatively stable environment, production of many clonal offspring is advantageous. Asexual reproduction is also favored by some plants and animals under stressful conditions, when mates or pollinators may be scarce.
Sexual reproduction introduces genetic diversity, which is generally advantageous. Genetically diverse populations are better able to tolerate environmental changes and are less susceptible to catastrophic losses when changes do occur. Genetic variation is the core of evolution by natural selection, and has produced the marvelously adapted organisms on Earth today.
Why is sexual reproduction advantageous?
D is the correct answer. Choices A, B, and C all refer to asexual reproduction.