 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson, you will review genetic engineering. Scientists, regardless of their specialization, need to possess a basic level of science literacy across all disciplines. This lesson provides an overview of the major concepts pertaining to genetic engineering that all students of the sciences should know. The chapters that follow will focus in greater detail on these ideas.
 Once the idea of chromosomes carrying genetic information had been put forth by Sutton in 1903, scientists set out to determine just what chromosomes were and how they worked. Within the next 50 years, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) had been identified as the molecule carrying the code and the exact structure of the double helix was worked out. Fifteen years later, the genetic code was cracked. By the early 1970s, restriction enzymes and polymerases were discovered; the polymerase change reaction (PCR) was developed in the mid-1980s, and the field of genetic engineering was born. DNA is replicated in living things when an enzyme called DNA polymerase builds complementary strands from free nucleotides in the cell nucleus. Restriction enzymes occur naturally in bacteria to help them cut up viral DNA and render it harmless. Once biologists understood the mechanisms of these enzymes, they were able to build DNA strands in tubes. The first genetic engineers recognized that restriction enzymes could also be used to isolate gene sequences by cutting the DNA strand in the right place. By cutting DNA to produce a template for a desired gene product and using polymerases to build complementary strands, designer genes became a reality.Transgenic organisms are produced using recombinant DNA (rDNA), which is produced from more than one organism. Bacteria are the most common transgenic organisms and are used by the pharmaceutical industry to produce medicinal products, such as human growth hormone and insulin. Plasmids can be used to insert the human gene into the bacterial genome. The bacteria then are stimulated to produce the protein. In some cases, viral vectors may be used to insert the foreign gene.
Once the idea of chromosomes carrying genetic information had been put forth by Sutton in 1903, scientists set out to determine just what chromosomes were and how they worked. Within the next 50 years, deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) had been identified as the molecule carrying the code and the exact structure of the double helix was worked out. Fifteen years later, the genetic code was cracked. By the early 1970s, restriction enzymes and polymerases were discovered; the polymerase change reaction (PCR) was developed in the mid-1980s, and the field of genetic engineering was born. DNA is replicated in living things when an enzyme called DNA polymerase builds complementary strands from free nucleotides in the cell nucleus. Restriction enzymes occur naturally in bacteria to help them cut up viral DNA and render it harmless. Once biologists understood the mechanisms of these enzymes, they were able to build DNA strands in tubes. The first genetic engineers recognized that restriction enzymes could also be used to isolate gene sequences by cutting the DNA strand in the right place. By cutting DNA to produce a template for a desired gene product and using polymerases to build complementary strands, designer genes became a reality.Transgenic organisms are produced using recombinant DNA (rDNA), which is produced from more than one organism. Bacteria are the most common transgenic organisms and are used by the pharmaceutical industry to produce medicinal products, such as human growth hormone and insulin. Plasmids can be used to insert the human gene into the bacterial genome. The bacteria then are stimulated to produce the protein. In some cases, viral vectors may be used to insert the foreign gene.

Some transgenic bacteria have been modified to assist in bioremediation, such as those used to quickly break down oil spills in the ocean. Organisms can be custom engineered to act on specific compounds. Many industrial pollutants might be broken down or neutralized using custom-made decomposers!
Many types of transgenic organisms have been produced and are used extensively in plant and animal agriculture. Many food crops have been genetically altered to have increased resistance to pests and disease, or to improve yield. Animals are being modified to have more lean meat and less fat. Some scientists are now trying gene pharming – the introduction of genes to produce drugs into food crops, such as tomatoes or bananas.
How are transgenic organisms used in bioremediation?
The correct answer is C. Bioremediation is about using living things to clean up the environment, genetically engineered or not!
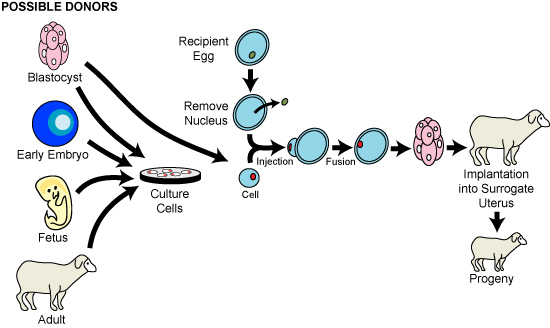
Cloning of animals is a type of genetic engineering. It involves putting a diploid nucleus into an egg from which the haploid nucleus has been removed. The diploid egg is then stimulated to undergo division, and the resulting embryo is implanted into a surrogate mother.
Which is an example of genetic engineering?
D is the correct answer. Choice A refers to the polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Choice B refers to biological warfare; smallpox is an example of an orthopoxvirus. Choice C refers to the ancient practice of selective breeding to produce a desired trait.