 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson we will review how to name aromatic hydrocarbons.
Aromatics are a special group of unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbons with delocalized electrons.The simplest is benzene or 1,3,5-cyclohexatriene.
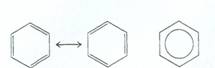
The circle represents the delocalized nature of the electrons where the double bonds are resonating between the carbons of the ring.
When naming molecules containing a benzene ring, the benzene ring becomes the main “Chain” and thus the last name. The rules for naming branches on cyclic hydrocarbons are the same with aromatics. When there are branches attached to a cyclic molecule, name the ring structure, add the name(s) of the branches, then tell the location(s) of the branches. When there is only one branch, it is always be located on the number one carbon (any one could be designated as number one), so no location number is needed.
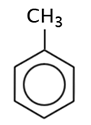 |
methyl benzene |
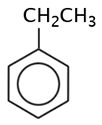 |
ethyl benzene |
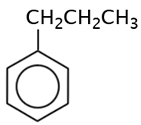 |
propyl benzene |
When multiple branches are located on a benzene as with all cyclic hydrocarbons you can start the numbering with any carbon of the ring and go in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction.
With aromatics when a benzene ring has branches in the 1st and 2nd positions they are referred to as being in the “ortho-“ position (“o-“ is used), when in the 1st and 3rd positions it is referred to as being in the “meta-“ position (“m-“ is used) and when in the 1st and 4th positions it is referred to as being in the “para-“ position (“p-“ is used).
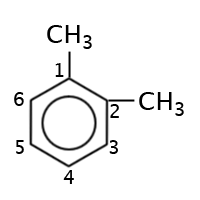 |
1,2-dimethylbenzene, ortho-dimethylbenzene or o-dimethylbenzene |
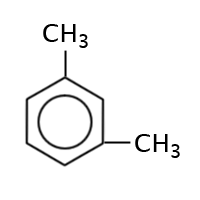 |
1,3-dimethylbenzene, meta-dimethylbenzene or m-dimethylbenzene |
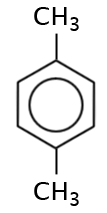 |
1,4-dimethylbenzene, para-dimethylbenzene or p-dimethylbenzene |
The delocalization of the electrons in the benzene ring causes great stability and therefore makes it less reactive than most other alkenes and alkynes. Also, its non-polar nature had made it a frequently used solvent. However, it has been found to be both a poison and a carcinogen, so its usage has declined.
When benzene is a branch it is called “phenyl-.”
What is the name of the following molecule?
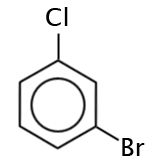
The correct answer is D. Both B and C are correct. Having branches in the 1 and 3 position of a benzene ring are referred to as being “meta-“ which is abbreviated as “m-.”
What is the name of the following molecule?
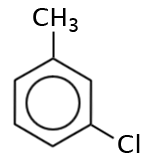
The correct answer is A. It could also be called, m-chloromethylbenzene or meta-chloromethyl benzene.