 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson, we’ll review naming halogenated hydrocarbons and hydrocarbon reactions.
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contain one or more halogen atoms (bromine, chlorine, fluorine or iodine) which have been substituted for a hydrogen atom.
When naming hydrocarbons that contain one or more halogen atoms find the longest carbon chain that contains the halogen-bearing carbon(s). Name the carbon chain and treat the halogens as branches, using “bromo-“ for bromine, “chloro-“ for chlorine, “fluoro-“ for fluorine, and “iodo-“ for iodine. The halogens are listed in alphabetical order preceding the carbon chain name yet they are numbered so as to give the lowest possible sum of the numbered branches after being placed in alphabetical order. If there is more than one of a kind of a particular halogen the Greek prefix (“di-,” “tri-,” “tetra-,” etc.) is inserted between the numbers for the halogens and the halogen’s name, after the halogen(s) have been placed in alphabetical order.
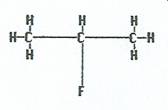 |
2-fluoropropane |
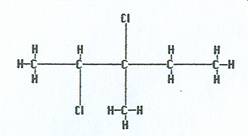 |
2,3-dichloro-3-methylpentane |
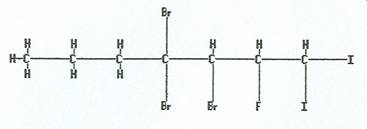 |
3,4,4-tribromo-2-fluoro-1,1-diiodoheptane |
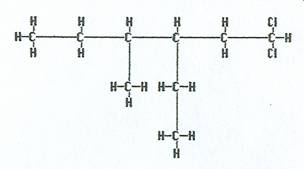 |
1,1-dichloro-3-ethyl-4-methylhexane |
What is the name of the following molecule?
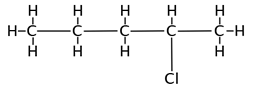
The correct answer is B. The longest carbon chain containing the halogen is the root name and the halogen is named using “chloro-“ for chlorine, “fluoro-“ for fluorine, etc. The halogens are treated as branches and given the lowest possible number.
What is the name of the following molecule?

The correct answer is D. The longest carbon chain containing the halogens is the root name; the halogens are named using “chloro-“ for chlorine, “fluoro-“ for fluorine, etc. The halogens are listed in alphabetical order.
Substitution reactions occur when one or more hydrogen(s) are replaced by a reactant.
For example:
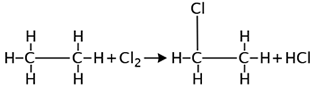
Because of the double bond, alkenes are more reactive than alkanes.
For example:
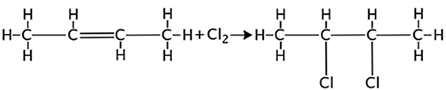
For example:
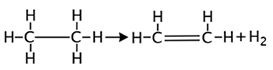
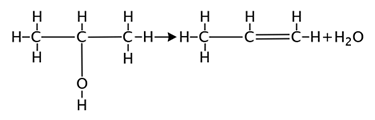
H2O, HNO2 and H-halide are often the products of elimination reactions.
For example:
What type of reaction is shown below?

The correct answer is D. This is a substitution reaction because one chlorine atom has been substituted for a hydrogen atom of the hydrocarbon.
What type of reaction is shown below?
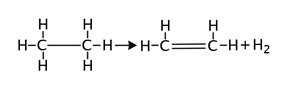
The correct answer is B. This is a dehydrogenation reaction because a hydrogen molecule has been eliminated from ethane.