 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson we will examine how alkenes, alkynes, cycloalkanes and cycloalkenes are named.
Alkenes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more double bonds. To name alkenes find the longest chain of carbon atoms that contains the double bonds. The stem of the name is the number of carbons in the chain ( “eth,” “prop,” “but,” etc.) followed by “ene” to indicate that the molecule contains a double bond. Next, number the carbons in the chain from both directions, left to right and right to left; choose the way that gives the lowest number(s) to the carbon(s) where the double bond starts.
This molecule would be 1-pentene.
It is five carbons with a double bond between the first and second carbon atoms (counting right to left).
If there are multiple double bonds then the name details how many carbons in the chain, again numbering in both directions using the sum of the numbers of where the double bonds start to determine the direction in which to go. Include the Greek prefix “di,” “tri,” “tetra,” etc to indicate the number of double bonds.
The name of this molecule is 2,3-hexadiene. The “hex” comes from the fact that there are six carbons in the chain. The numbers show where the double bonds start. The numbers 2 and 3 would be used since 2 plus 3 equals 5 which is smaller than 3 plus 4 which equals 7. The “di” in the middle of the name indicates that there are two double bonds. The “a” is inserted for pronunciation because of adding a consonant “d” in “di” after the “x” in “hex.”
When there are branches in alkenes they are handled the same way as with alkanes except the numbering of the double bond(s) dictates the direction in which the carbons in the chain are numbered. The starting of the double bonds needs to be as low as possible and once the direction is determined it is used throughout the name.
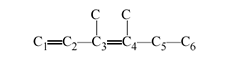
The name of this molecule is 3,4-dimethyl-1,3-hexadiene. The 3 and 4 indicate the location of the one-carbon branches. The “di” methyl indicates that there are two one-carbon branches. The 1 and 3 show the start of the double bonds. The “hex” indicates that here are six carbon atoms in the longest chain. The ending of “-ene” indicates that there are double bonds. The “di” in the middle indicates that there are “di” double bonds.
Naming alkynes is the same as naming alkenes except the ending “yne” is used instead of “ene.”
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain one or more triple bonds.
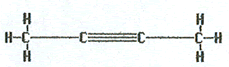
The name 2-butyne would indicate that the molecule has four carbons in a chain with a triple bond between carbons 2 and 3.
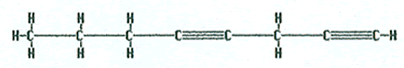
The name 1,4-octadiyne would indicate that the molecule has eight carbons due to the “oct.” The “di” indicates that there are two triple bonds. The 1 and 4 shows the location of the triple bonds. The “a” in the middle is to make the name easier to pronounce.
Cycloalkanes are hydrocarbons whose carbon atoms are arranged in a ring or cyclic structure. In order to name cycloalkanes count the number of carbon atoms in the ring and add the prefix “cyclo.”
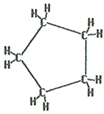
The name of this molecule is cyclopentane. The “cyclo” shows that it has a ring structure. The “pent” indicates there are five carbons. The “ane” ending indicates the carbon atoms are singly bonded together.
When there are branches attached to a cyclic molecule, name the ring structure, add the name(s) of the branches, and then tell the location(s) of the branches. You can start the numbering with any carbon of the ring and go in either a clockwise or counterclockwise direction.
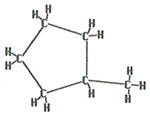
The name of this molecule is methylcyclopentane. Note that no number is needed with this molecule as no matter where the methyl group is it could be considered to be on the number one carbon.
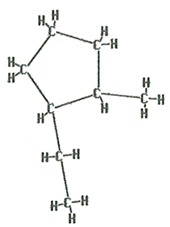
The name of this molecule is 1-ethyl-2-methylcyclopentane. There are 5 carbons in a ring with single bonds between them, therefore it is a cyclopentane. Since there are both an “ethyl” branch and a “methyl” branch they are listed in alphabetical order and numbered to give the lowest sum.
Cycloalkenes are hydrocarbons with carbon atoms arranged in a ring or cyclic structure and which have one or more double bonds between the carbon atoms. In order to name cycloalkenes count the number of carbon atoms in the ring, add the prefix “cyclo,” and include the suffix “ene” instead of “ane.” The location of the double bond(s) establishes the numbering of the carbon atoms in the ring. They get the lowest numbers even if the branches get higher numbers. Again one can go either clockwise or counterclockwise to get the lowest numbers. Also, if there is more than one double bond one needs to insert the Greek prefixes such as “di,” “tri,” “tetra,” etc. to indicate how many double bonds there are in addition to the numbers showing their location.
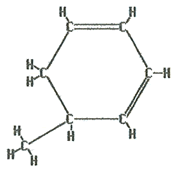
The name of this molecule is 5-methyl-1,3-cyclohexadiene. The cyclohexadiene indicates there are six carbons in a ring with two double bonds. One double bond is between the 1st and 2nd carbons and one is between the 3rd and 4th. Also, there is a one carbon branch (methyl) on the 5th carbon. Notice that in order to give the double bond the lowest possible numbering the branch received a higher number.
What is the name of this molecule?

The correct answer is D. The chain name is “pentene” because there are five carbons in the chain with a single double bond. The number 1 before “pentene” tells the location of the start of the double bond. The “methyl” indicates there is a one-carbon branch, the 4 tells that the branch is located on the 4th carbon of the chain. Remember that the multiple bond dictates the direction of the number of the carbons in the chain and once the direction is determined it is used throughout the name.
What is the name of this molecule?

The correct answer is D. The “cycloheptadiene” results from the seventh carbon, two double bond ring. The numbers 1 and 2 are to give the double bonds the lowest sum. You can go either clockwise or counterclockwise. Going counterclockwise the branch is on the 6th carbon; going clockwise the branch would be on the 5th carbon, so the 5th carbon is used.