username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson we will study polymers and how they form.
Polymers are macromolecules made up of small repeating units of molecules. The small repeating units are called monomers. Proteins are a class of polymers which are composed of up to several thousand amino acid monomers. Carbohydrates are another class of polymers with the general formula of CxH2xO. Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) is also a polymer. It has a molecule weight of several billion grams per mole.
There are several ways in which the monomers get together to form the polymer. We will discuss two ways:
Addition polymerization occurs when the monomers are “added” together through their unsaturated bonds in order to form a polymer.
Examples include:
|
Vinyl chloride monomers
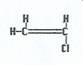 |
Added together they make polyvinyl chloride (PVC)
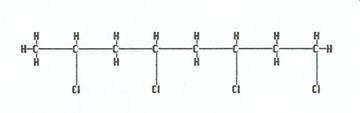 |
|
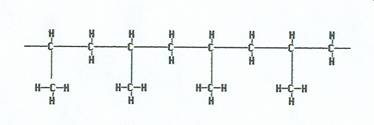
Propylene
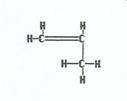 |
Monomers are added together to yield polypropylene
 |
|
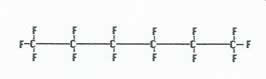
Tetrafluoroethene
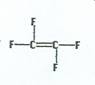 |
Monomers are added together to yield teflon
 |
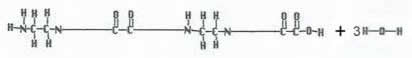
Condensation polymerization occurs when the monomers are brought together to form a polymer and a small molecule, such as water.
For example:
C2H5NO2 + C2H5NO2 → C4H8N2O3 + H20

(C2H7N2)2 + (C2H2O4)2 → C8H12N4O5 + H20