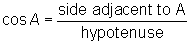username@email.com
username@email.com
In this next section, we’ll examine some components of a triangle, and review the methods to determine the perimeter and area of triangles.
We’ll also refresh your memory about the Pythagorean Theorem (and Pythagorean triples) and delve into some basic trigonometry.
Perimeter is a two-dimensional measure of the distance around the figure. For any polygon, the perimeter is simply the sum of the lengths of all of its sides.
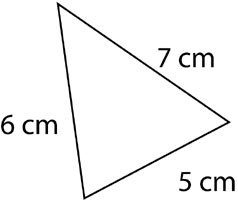
Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of this triangle is 5 cm + 6 cm + 7 cm, or 18 cm.
It’s just that easy!
Perimeter is a two-dimensional measure, so it uses units like centimeters, meters, inches, or feet.
What is the perimeter of triangle ABC below?
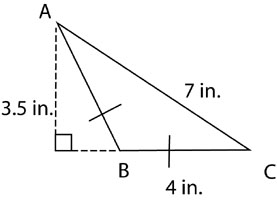
Choice B is correct. Since the triangle is isosceles, it has two legs that measure 4 inches each, and a base that measures 7 inches. Therefore, the perimeter is 4 in. + 4 in. + 7 in., or 15 in. Choice A is incorrect, because the segment labeled 3.5 in. is not a side of triangle ABC.
The area of a two-dimensional figure is the number of square units it contains. You’ve probably heard of an apartment or house being measured in square feet (ft2). Other examples of square units are square inches (in2) and square centimeters (cm2).
The area of a triangle is given by the formula 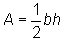 , where b is the base and h is the height.
, where b is the base and h is the height.
It is important to remember that the base and the height must be perpendicular.
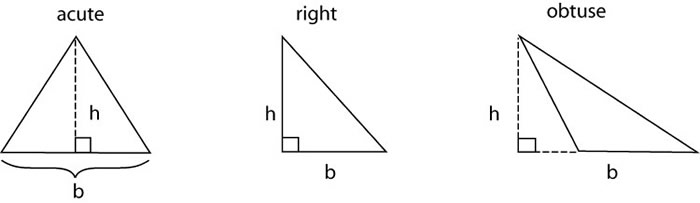
What is the area of triangle ABC below?
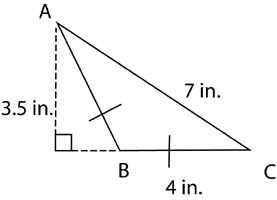
Choice A is correct. The base has a length of 4 in., and the height has a length of 3.5 in., so the area is 7 in2. If you answered C, you may have forgotten to multiply the product of the base and height by one-half. If you answered D, you may have calculated the perimeter of the triangle.
Think about why the formula for area contains 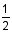 . We’ll address this in a later section.
. We’ll address this in a later section.
This is probably the most popular theorem in all of geometry. In fact, it’s pretty important algebraically, as well.
The right triangle below has legs of length a and b, and a hypotenuse of length c.
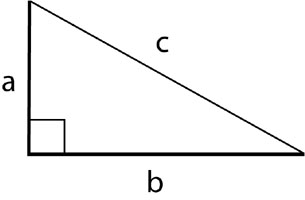
Legs and Hypotenuse
The Pythagorean Theorem gives the relationship between the lengths of these sides. It says: The sum of the squares of the lengths of the legs of a right triangle is equal to the square of the length of the hypotenuse. (Note: This is only true for right triangles. If the lengths of the sides of any triangle satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem, the triangle must be a right triangle.)
We can take “square” in its algebraic and its geometric senses. Algebraically, the Pythagorean Theorem looks like this:
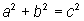
All right, let’s see how to use the theorem. Suppose the two legs of a right triangle measure 3 in. and 4 in. What is the length of the hypotenuse? In the theorem, a and b represent the lengths of the legs, so let a = 3 and b = 4. Now find c:
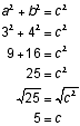
A 3-4-5 triangle is the most popular Pythagorean triple. A Pythagorean triple is a set of three positive integers that satisfy the Pythagorean Theorem. Multiples of Pythagorean triples are also Pythagorean triples. In other words, since 3-4-5 is a Pythagorean triple, so is 6-8-10 and 9-12-15. Another Pythagorean triple is 5-12-13.
Most, if not all, test questions related to the Pythagorean Theorem involve Pythagorean triples, because they’re easier to compute and they don’t involve irrational numbers (like √2 or 3√5).
One leg of a right triangle is 8 cm long and its hypotenuse measures 17 cm. What is the length of the remaining leg?
Choice C is the correct answer. The Pythagorean Theorem states that a2 + b2 = c2, where a and b are the lengths of the legs of a right triangle, and c is the length of the hypotenuse. In this problem, one leg measures 8 cm and the hypotenuse measures 17 cm. So, let a = 8 and c = 17, and find b. The other leg has length 15 cm. Did you figure out that 8-15-17 is also a Pythagorean triple?
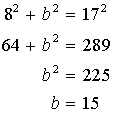
Trigonometry literally means “triangle measure.” The trigonometry (or “trig”) that we’ll explore here is restricted to right triangles, so sometimes it’s called right triangle trigonometry.
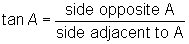
A trig function is one that relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle to one of its angle measures. In this lesson, we’ll explore the three basic trig functions: sine, cosine, and tangent.
The sine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the leg opposite the angle to the length of the hypotenuse.
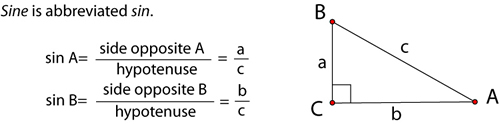
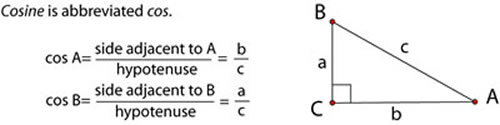
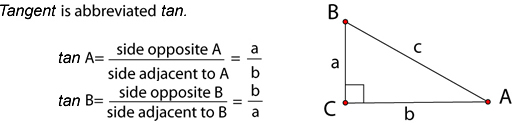
Example 1: The base of this right triangle is 10 in. long. What is its height, h?
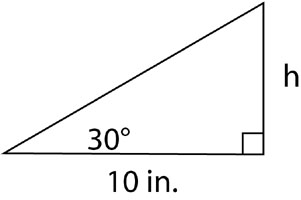
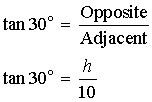
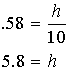
Example 2: Now let’s find the length of the hypotenuse. We could use the fact that there are 180° in a triangle to find the measure of the other acute angle, or we could simply use the angle we’re given. If we do that, we have an angle and the sides opposite and adjacent to it. We want to find the hypotenuse, so we could use either sine or cosine.
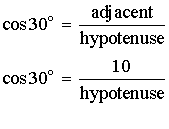
Therefore, the  , or about 11.5 in.
, or about 11.5 in.
Which of the following is the best approximation for leg x in the triangle below? Note that the cos50° is .574, the sin50° is .766, and the tan50° is 1.19.
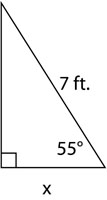
Choice A is the correct answer. We’re given an angle measure and the hypotenuse. We want to find the length of the side adjacent to the given angle, so we need a trig formula that relates the measure of an angle to the adjacent side and to the hypotenuse. The cosine function does that. The value of x is about 4 ft. If you answered B, you may have used the sine function instead of the cosine function.
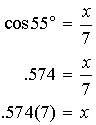
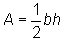 , where b is the base and h is the height, and the base and height are perpendicular.
, where b is the base and h is the height, and the base and height are perpendicular.