 username@email.com
username@email.com
In this lesson, we’ll explore transformations, which are changes to the size, shape, location, or orientation of a figure.
Let’s investigate three types of transformations: translations, reflections, and rotations.
A figure undergoes a translation when it slides a certain distance in a certain direction. The translated figure is called the image of the original figure. It is congruent to the original figure.
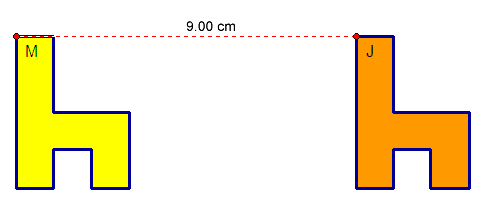
The yellow figure (M) has been translated a distance of 9.00 cm to the right. The orange figure (J) is the translated image of the yellow figure (M).
A reflection is a transformation that produces a mirror image of the original figure by flipping it across a line. While the reflection changes the object’s orientation (top and bottom, left and right), the reflected image is congruent to the original figure.
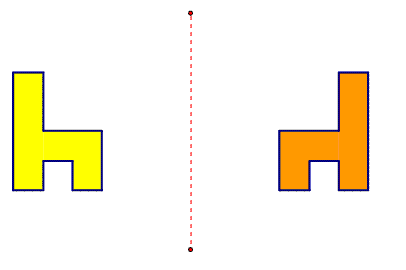
The yellow figure (left) has been reflected over the dotted line to produce the orange mirror image (right).
The image below shows a figure that has a property called bilateral symmetry. The figure can be divided in half by a line of symmetry so that one side is a mirror image of the other side. In fact, this figure has many lines of symmetry, but only one is drawn here. All regular polygons have bilateral symmetry.
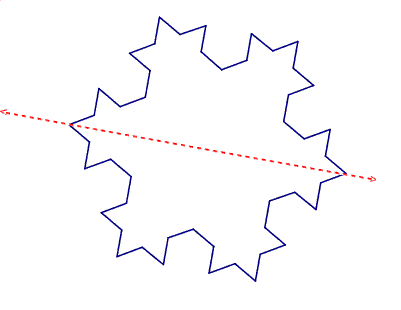
Bilateral Symmetry
A rotation is a transformation that rotates an object around a point. While the rotation changes the object’s orientation, the rotated image is congruent to the original figure.
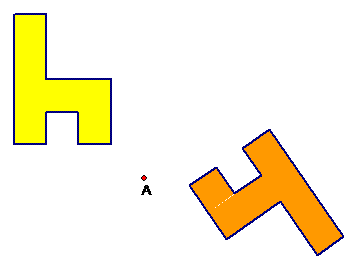
The yellow figure has been rotated 215° around point A to produce the orange figure.
The equilateral triangle below has a property called rotational symmetry. A figure has this property if it can be rotated around a point by less than 360° and the object appears unchanged. This figure can be rotated 120° or 240° and it will appear unchanged.
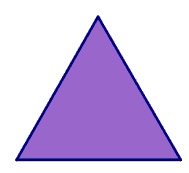
Polygon with Rotational Symmetry
Which of these is an example of a translation?
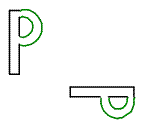
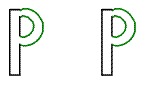
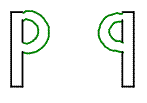
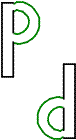
The correct answer is B. A translation is a transformation that slides a figure a certain distance in a certain direction. Choice A shows rotation, which rotates a figure around a given point. Choice C shows a reflection, which produces a mirror image of a figure over a line. Choice D doesn’t show anything.