 username@email.com
username@email.com
We will now cover some of the important aspects of plant biology, culminating in an in depth look at plant physiology.
We have reviewed the physiology of animals in depth, going over animal organization and function from cell to tissue to organ to organ system. We will now turn our attention to plants.
Plants have the following characteristics:
Plants are divided into two groups: nonvascular and vascular. Nonvascular plants, which include mosses and liverworts, have simple conducting tissue that does not differentiate into roots, stems, and leaves. Vascular plants have tissue that is differentiated into roots, stems, and leaves to facilitate the movement of water and other materials throughout the body of the plant.
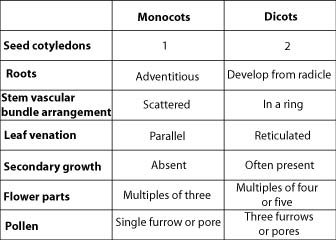
Vascular plants are divided into seedless plants and seed plants. Seedless plants include ferns, horsetails, whisk ferns, and club mosses. These plants live close to water. Over time, as plants developed farther away from water sources, they developed seeds. Seeds permit an embryo to survive long periods of time in unfavorable conditions and to disperse an embryo from its parent plant. Seed plants are further divided into gymnosperms and angiosperms. Most living gymnosperms are conifers, producing their seeds in cones. Some examples are: pine, cedar, cypress, redwood, spruce, and fir trees. Angiosperms, such as roses, daisies, grasses, and sunflowers, reproduce with flowers. The flowers promote pollination. Finally, angiosperms are divided into monocots and dicots. This distinction is based on the number of cotyledons, or seed leaves on the plant embryo. Monocots evolved later than dicots.
The first land plants, still alive today, are
The correct answer is C, because A and B are seed plants, which came much later. Choice D is also incorrect because ferns also came much later, but between algae and seed plants. The first land plants were algae.
A seed is a sporophyte plant embryo surrounded by a protective coat. The parts of the embryo are named according to their point of attachment to the cotyledons. The epicotyl is the stem above the cotyledon, and develops into the plant stem. Below the cotyledon is the hypocotyl, which has a region, called the radicle, at its base. The radicle develops into the plant’s roots. The rest of the embryo consists of the food supply.

Roots have a simple structure. They lack external features and pith. The vascular bundles are at the center of the root. Epidermal cells cover the end of the root and those near the root tip produce slender projections called root hairs. Root hairs increase the surface area of the root and absorb water and minerals from the soil. There are three types of root systems:
A taproot system has a large central root called a taproot. The roots that branch from the taproot are usually much smaller. Most dicots have a taproot system. This root system can store sugars or starches. Some examples include carrots, radishes, beets, dandelions, oak trees, and hickory trees.

A fibrous root system is highly branched with roots that are about the same size. Most monocots have fibrous root systems. These systems are important in holding topsoil so that rain does not wash it away. Some examples include grasses and onions.

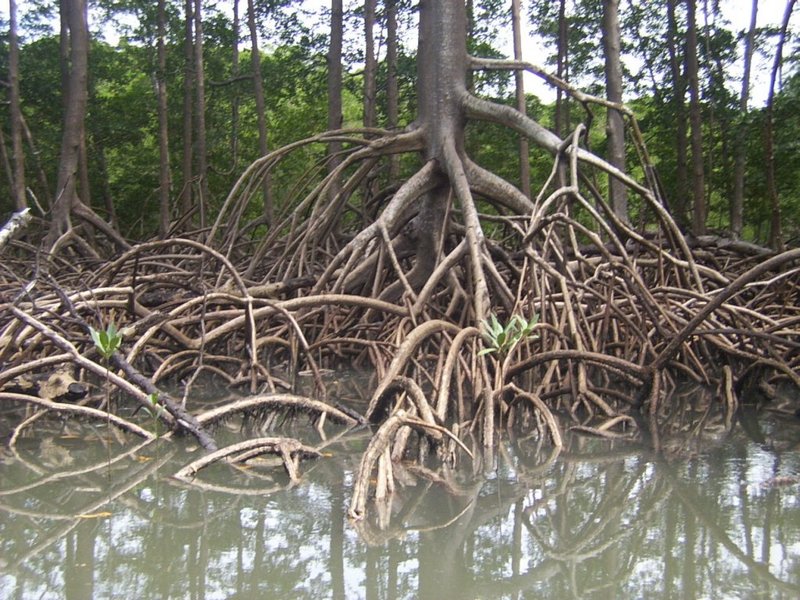
Adventitious roots grow above ground and provide support, as well as absorbing water. Two types of this root system are prop roots and aerial roots. Some examples include corn, mangroves, and orchids.

A primary root that grows longer and thicker is
The correct answer is B. A taproot is long and thick with shorter roots that branch off it. Choice A refers to the slender projections off root tips. Choice C and D are types of root systems.
Stems vary in size and shape from one plant species to another but all stems have two basic functions: holding leaves up in the sunlight and conducting various substances between roots and leaves. In addition, some stems store water and nutrients.
Stems have four basic types of tissue:
Vascular tissue in stems conducts water, nutrients, and other materials throughout the plant. The arrangement of this tissue in the stem differs in monocots and dicots. In monocots vascular tissue is scattered in bundles throughout the stem. In dicots it is arranged in a ring.
The places where leaves attach to a stem are called nodes. Internodes are the areas of stem between the nodes. Also at the nodes are lateral buds that grow into branches of the stem. There are two main types of stems: herbaceous and woody.
Herbaceous stems are flexible, relatively soft, and usually green in color.

Woody stems are stiff, contain layers of wood, and usually are not green in color.

Some stems are modified for other functions and include rhizomes, tubers, and bulbs.
Rhizomes are thick, fleshy, creeping stems that grow either alongside or beneath the surface of the ground. When winter frost kills the above-ground parts of plants, the rhizomes survive to grow again the following springs. Examples of plants with rhizomes are irises, canna lilies and some species of grasses.

Tubers are modified underground stems that are swollen with stored food, usually starch. The most common example of a tuber is the potato.

Bulbs have underground stems. The stem at the center is small. Most of the food stored is located in layers of leaves that wrap around and protect the stem. Examples of plants with bulbs include daffodils and tulips.
Which of the following is a modified stem?
C is the correct answer, because the potato has a modified stem called a tuber. Choices A and B are modified leaves. Choice D is a modified root.
The leaves of a plant are the world’s most important manufacturers of food. Most leaves have a basic structure of a large, flattened surface called the blade that is attached to the stem by a petiole.
Leaves with a single blade and petiole are simple leaves. Compound leaves have several blades, or leaflets.
Veins, which are strands of xylem and phloem tissue, run along the leaves.
Leaves are covered by a layer of tough epidermal cells and a waxy cuticle. Within the epidermis are small openings called stomata, which are formed by two specialized epidermal cells called guard cells. Gas exchange takes place through the stomata.

Most leaf tissue is composed of specialized cells called mesophyll. This tissue contains chloroplasts and performs most of the plant’s photosynthesis. The mesophyll is divided into two layers. The top layer consists of rows of closely packed, columnar cells and is called the palisade layer. The lower layer has loosely packed, spherical cells and is called the spongy layer.
Some plants have modified leaves specialized for protection, water conservation, climbing, and reproduction. Remember that most plant parts are basically modified leaves.
Openings that permit gases to enter and leave the leaf are called
The correct answer is B. Stomata are formed from guard cells and control gas exchange in leaves.
Flowers are the reproductive organs of angiosperms and usually produce both male and female gametes. Flowers are actually miniature stems that produce four kinds of specialized leaves: sepals, petals, stamens, and carpels. These leaves are arranged in circles and have been modified to serve different purposes.
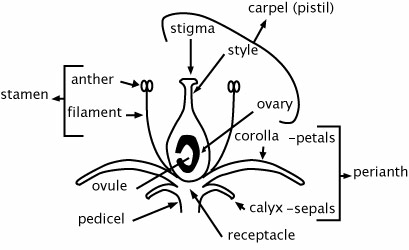
Flowers may or may not have all four parts, which classifies flowers into one of four categories:
Complete flowers have all four whorls of leaves. 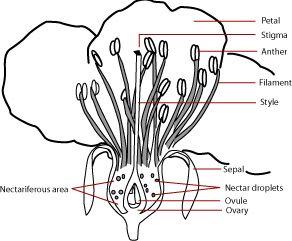
Complete flowers have all four whorls of leaves. 
Perfect flowers have both stamens and pistils. 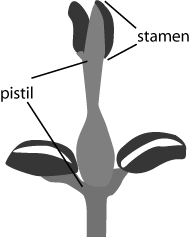
 Imperfect flowers lack either stamens or pistils.
Imperfect flowers lack either stamens or pistils.
Flower parts most involved with attracting pollinators are the
The correct answer is D, because the petals are usually brightly colored and have a fragrance to attract pollinators. Choice A is a female flower part and choice C is a male flower part, both of which have no qualities for attracting pollinators. Choice B, seeds, is the product of fertilization — long after pollinators are gone.