 username@email.com
username@email.com
The following lesson will examine whole numbers, rational and irrational numbers, integers, and their properties.
The counting numbers or natural numbers are the numbers 1,2,3,4,…. The whole numbers are the counting numbers plus zero. The integers are the whole numbers and all their opposites. Real numbers consist of rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers include whole numbers, fractions, finite or repeating decimals, and percents. Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be written as fractions since they are non-repeating and nonterminating decimals. A fraction is a ratio of two integers. The real numbers are the combination of the rational and irrational numbers. The only numbers that are not considered real numbers are the complex numbers which have the form ![]() .
.
A prime number is a number divisible only by 1 and itself. A composite number is a number with factors other than 1 and itself.
How do I convert between different forms of numbers?
We will study three conversions:
To convert from fractions to decimals, divide the numerator by the denominator.
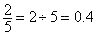
To convert from decimals to fractions, write the decimal as a fraction and reduce.
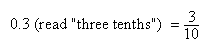

Think of a percent as meaning out of 100. To convert from fractions to percents, set the fraction equal to ![]() and solve for x.
and solve for x.
![]()
To convert from percents to fractions, put the percent over 100 and reduce.
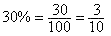
To convert from percents to decimals, move the decimal two places to the left and drop the percent sign. If no decimal place is shown assume the decimal place is at the right hand side of the number.
28% = 0.28
To convert from decimals to percents, move the decimal two places to the right and add a percent sign.
0.3 = 30%
Which of the following correctly shows 125% converted to a fraction?
The correct answer is B. To convert the percent to a fraction, place 125 over 100 and reduce.
![]()
Real numbers, decimals, fractions, and percents can be thought of as a point on a number line, where they are placed according to their value. The points on a number line are called coordinates, while the zero point is called the origin. The line extends infinitely on both sides of the origin, with positive numbers to the right and negative numbers to the left.
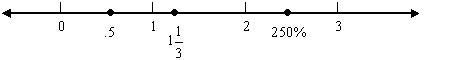
Which number line shows the correct placement of 1.25, ![]() , 250%?
, 250%?
The correct answer is D. First, convert all the numbers to the same form. 1.25 is already in decimal form, so convert ![]() to .75 by dividing the numerator by the denominator. Then convert 250 % to 2.50, by moving the decimal two places left and removing the percent sign. The points that should be graphed are .75, 1.25, and 2.50. Choice D shows the correct placement of the numbers on the number line.
to .75 by dividing the numerator by the denominator. Then convert 250 % to 2.50, by moving the decimal two places left and removing the percent sign. The points that should be graphed are .75, 1.25, and 2.50. Choice D shows the correct placement of the numbers on the number line.
Between every two real numbers, there are an infinite number of rational and irrational numbers.
Change numbers to the same form to easily see where they fit on the number line.
Which number line shows the correct number placement?

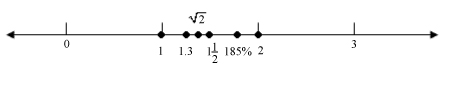

The correct answer is C. Each number is changed to a decimal or a decimal approximation; the numbers become 1, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5, 1.85, and 2. Place these numbers on the number line.
The associative property of addition states that the way you group a set of numbers does not affect the sum. For example, ![]() .
.
The associative property of multiplication states that the way you group a set of numbers does not affect the product. For example,![]() .
.
The distributive property states that the for any numbers a, b, and c, ![]() . For example,
. For example, ![]() .
.
The commutative property of addition states that the order in which you add a set of numbers does not affect the sum. For example, ![]() .
.
The commutative property of multiplication states that the way you group a set of numbers does not affect the product. For example, ![]() .
.
While the commutative and associative properties work for addition and multiplication, they do not work for subtraction and division. When in doubt, use a simple example to decide.
Irrational numbers are numbers that cannot be written as a fraction since they are non-repeating and non-terminating numbers. Examples of irrational numbers are ![]() and
and ![]() . It is helpful to use approximations of irrational numbers in problem situations.
. It is helpful to use approximations of irrational numbers in problem situations.
A support beam is needed for a 10 ft square wall. The beam will form the diagonal of the square. About how long will the beam be?
The correct answer is B. To find the length of the diagonal of a square, use the Pythagorean theorem. Since the legs of the triangle have the same length, both a and b are 10. Substitute into the Pythagorean Theorem and solve for c.

Use the approximation![]() , but remember that
, but remember that ![]() is not really
is not really ![]() .
.
![]()